Pahvantia hastata
Vendor: Gold Bugs
SKU Number: SQ2630746
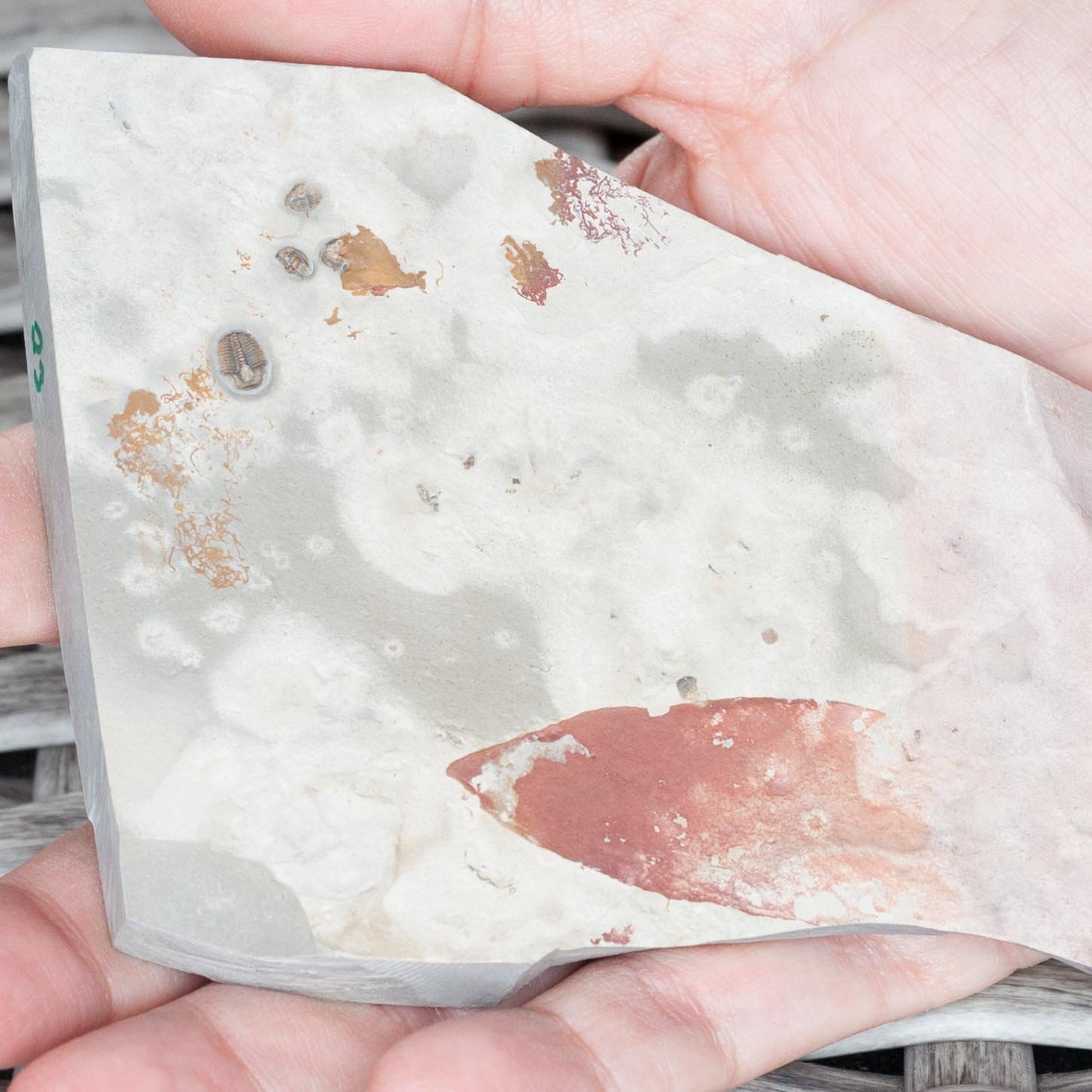
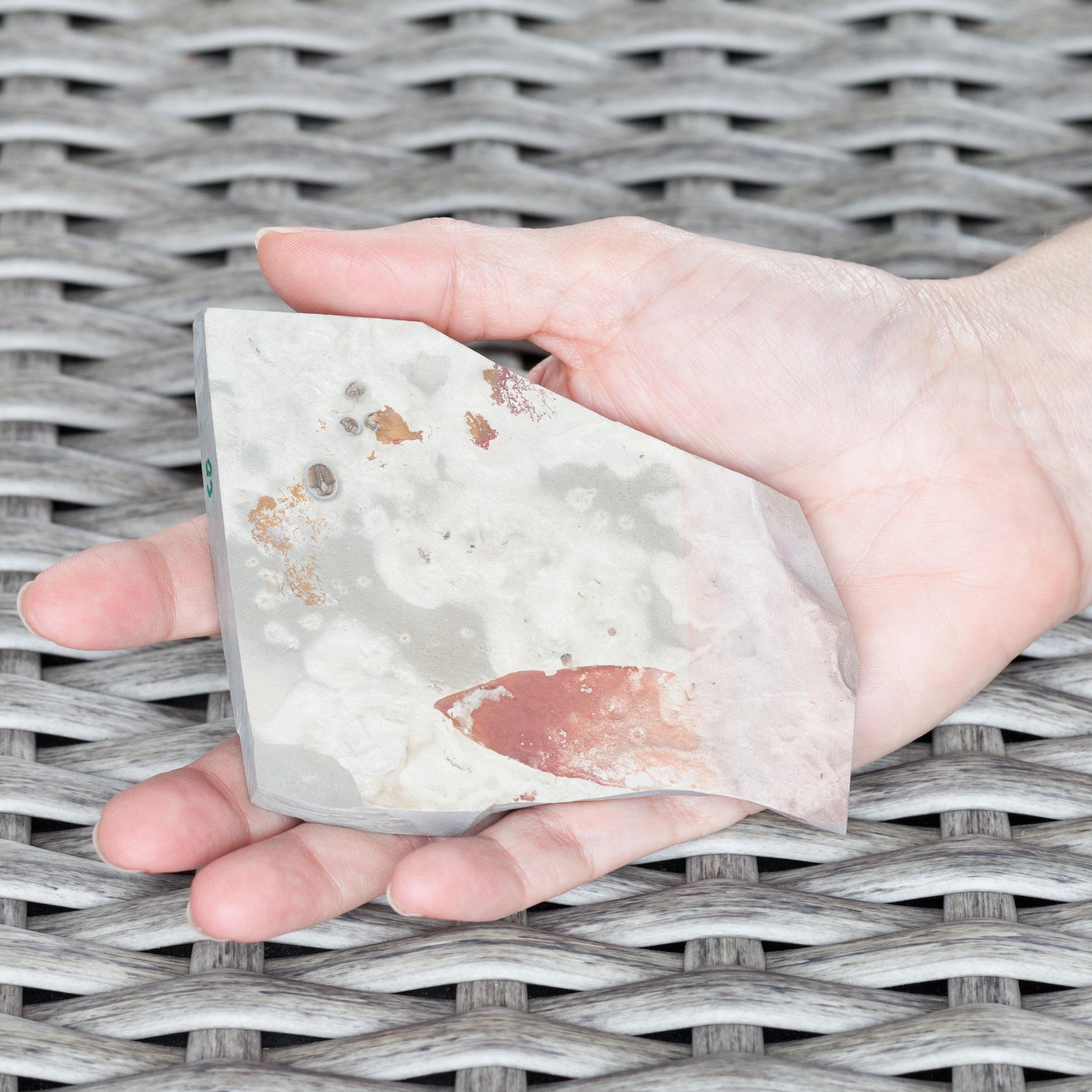
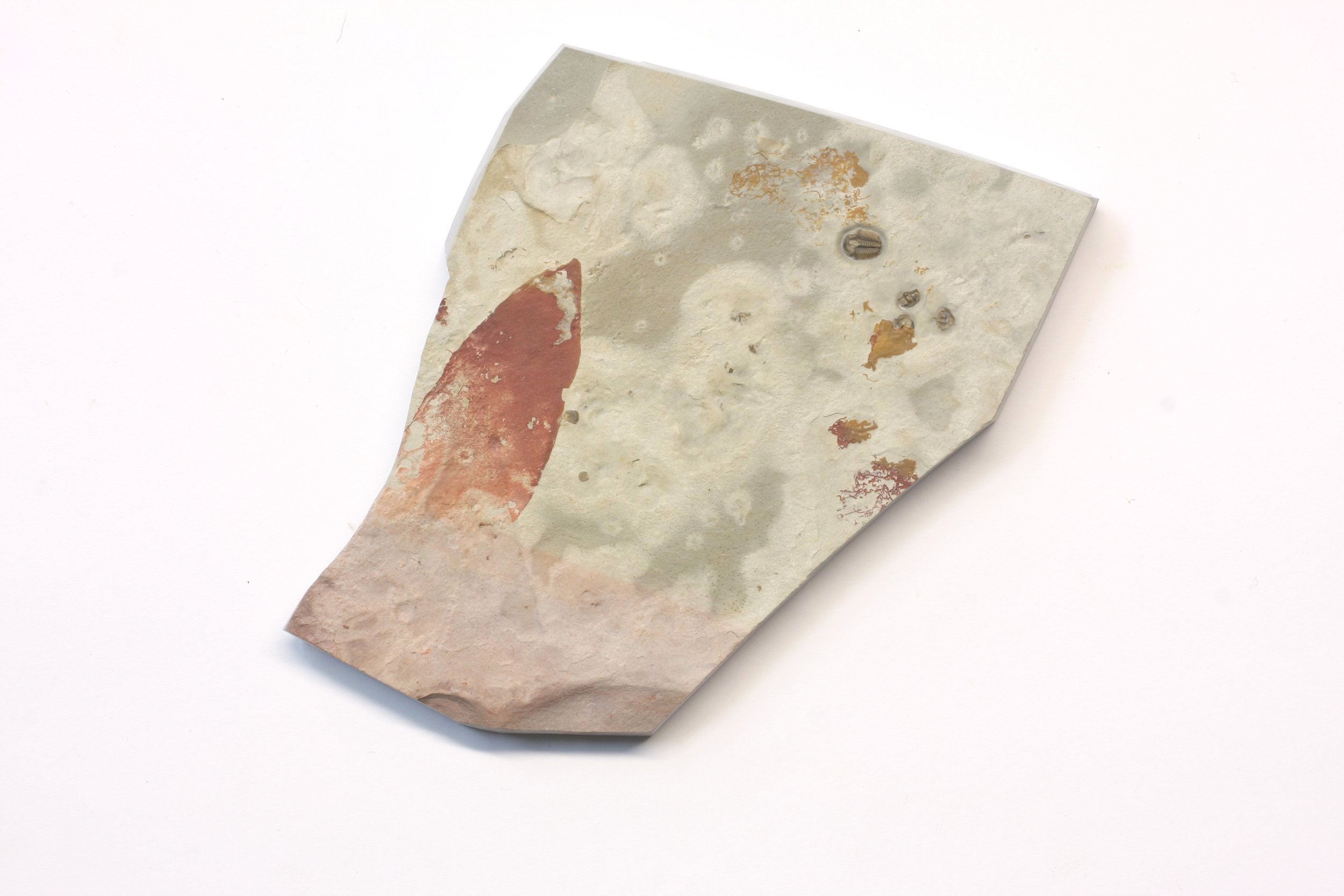
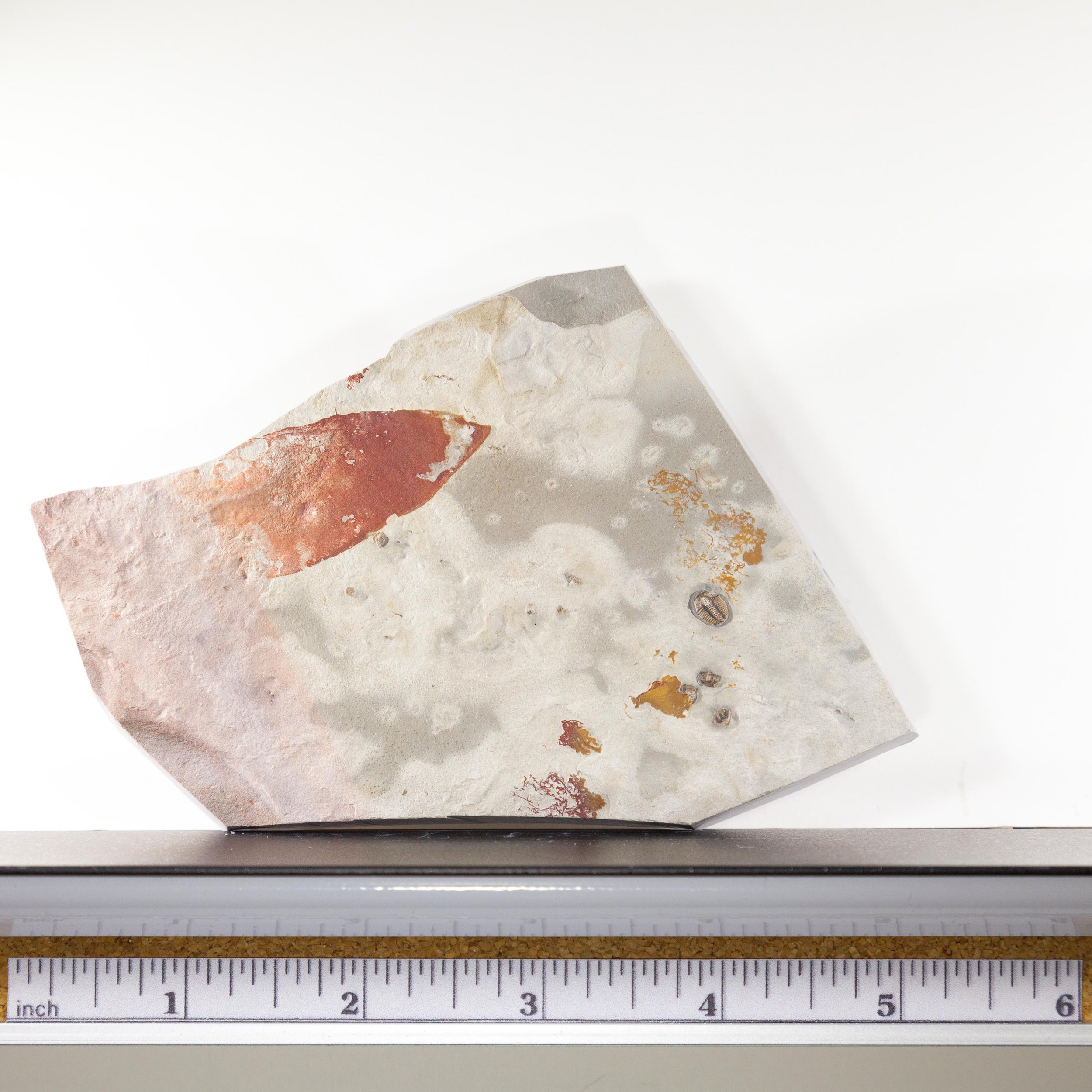
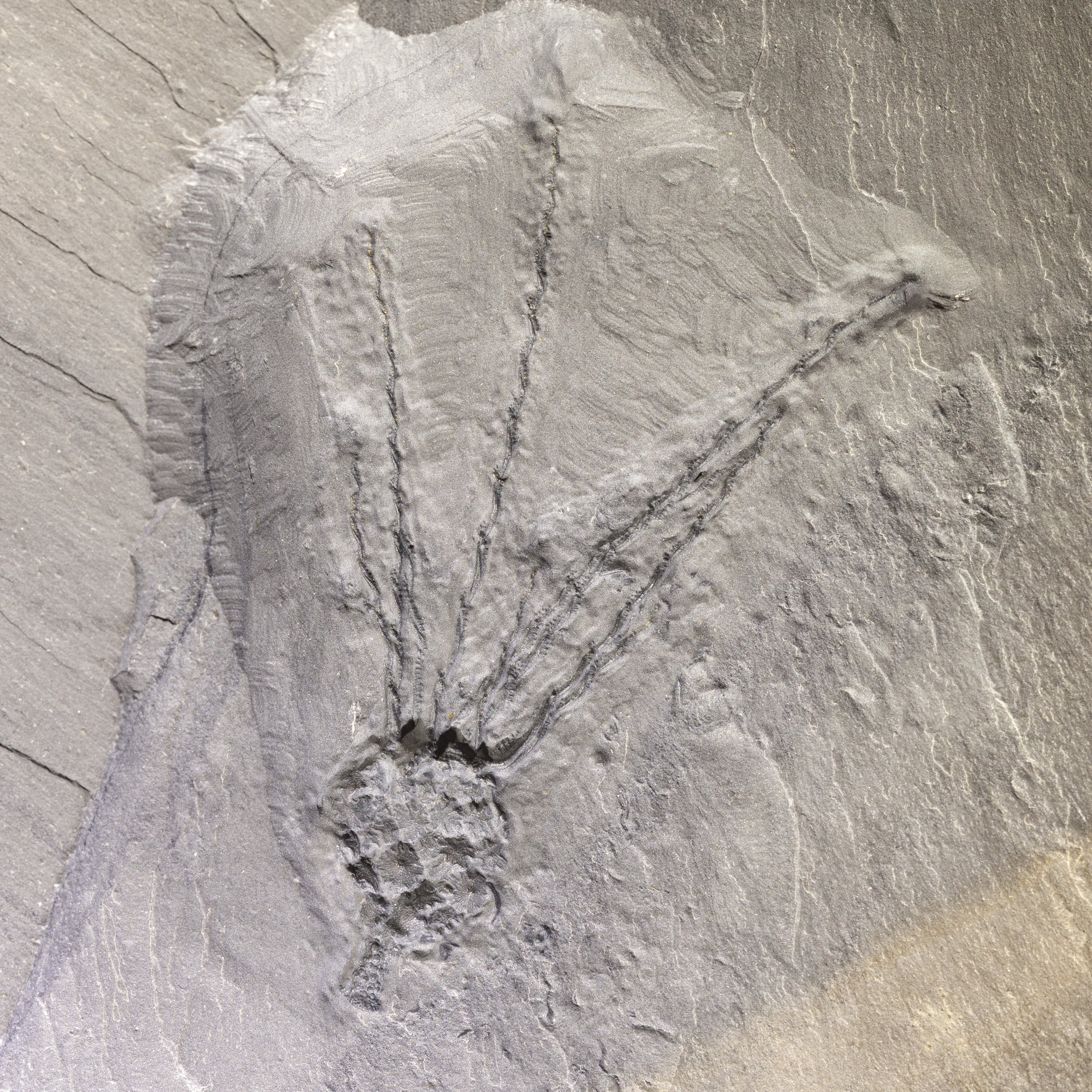
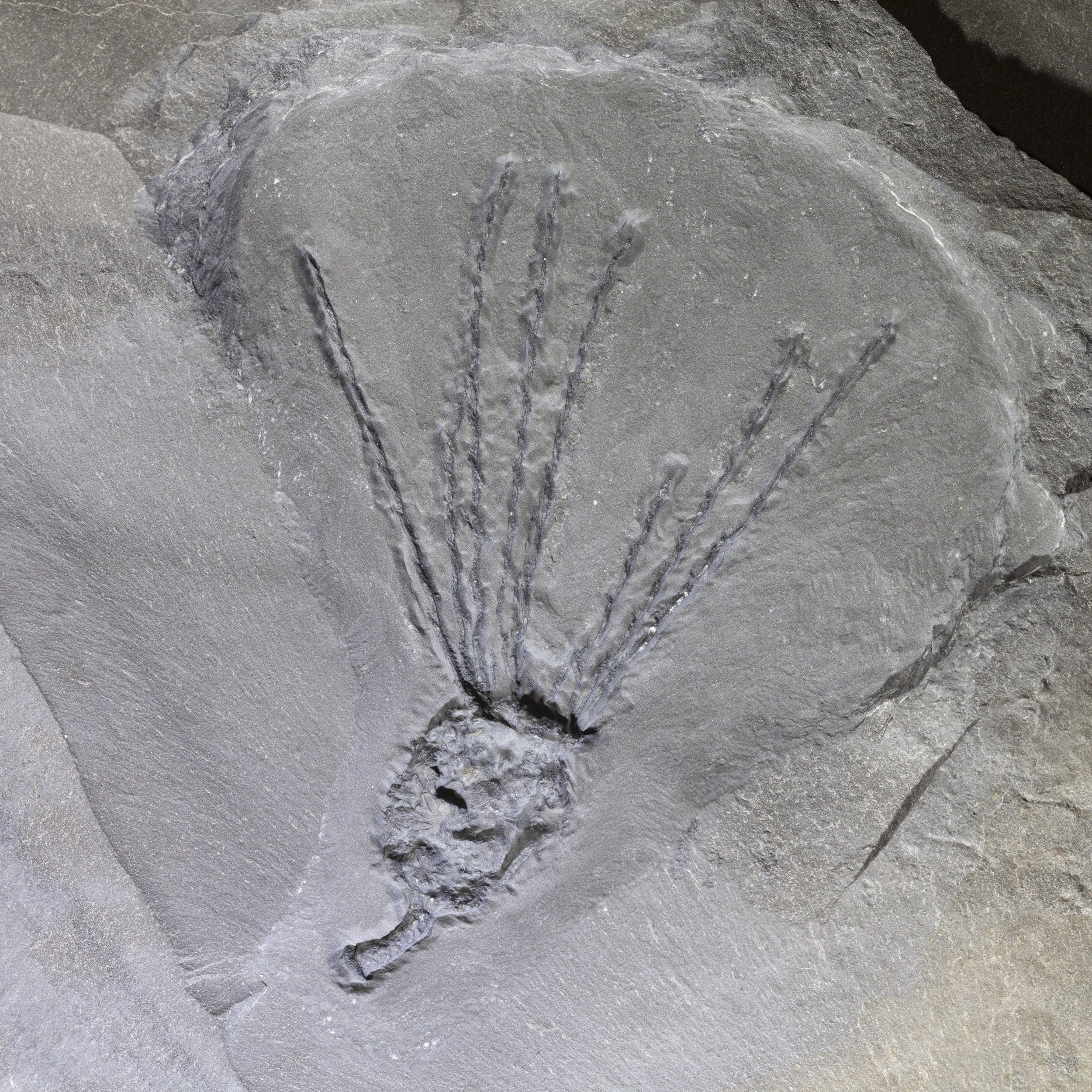
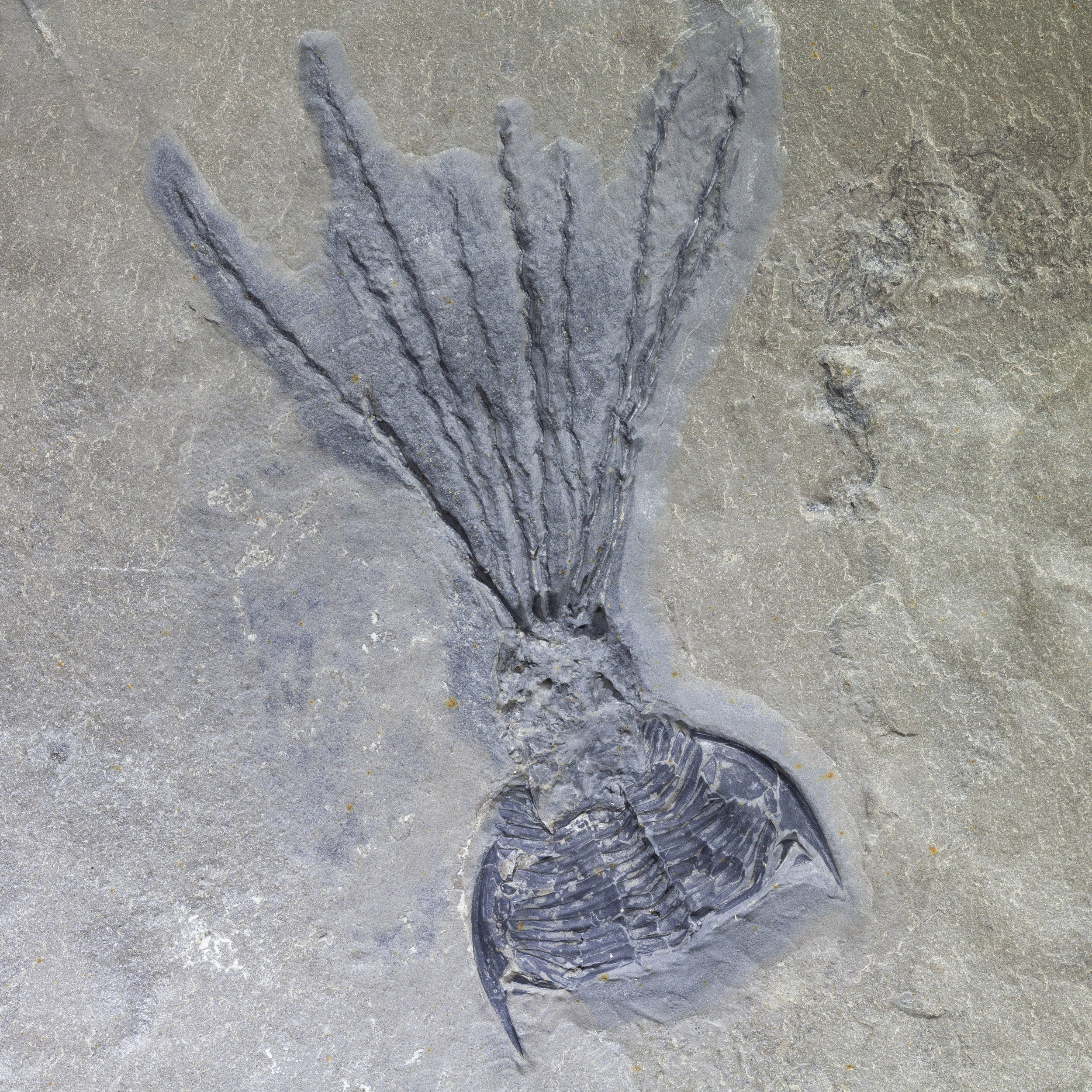
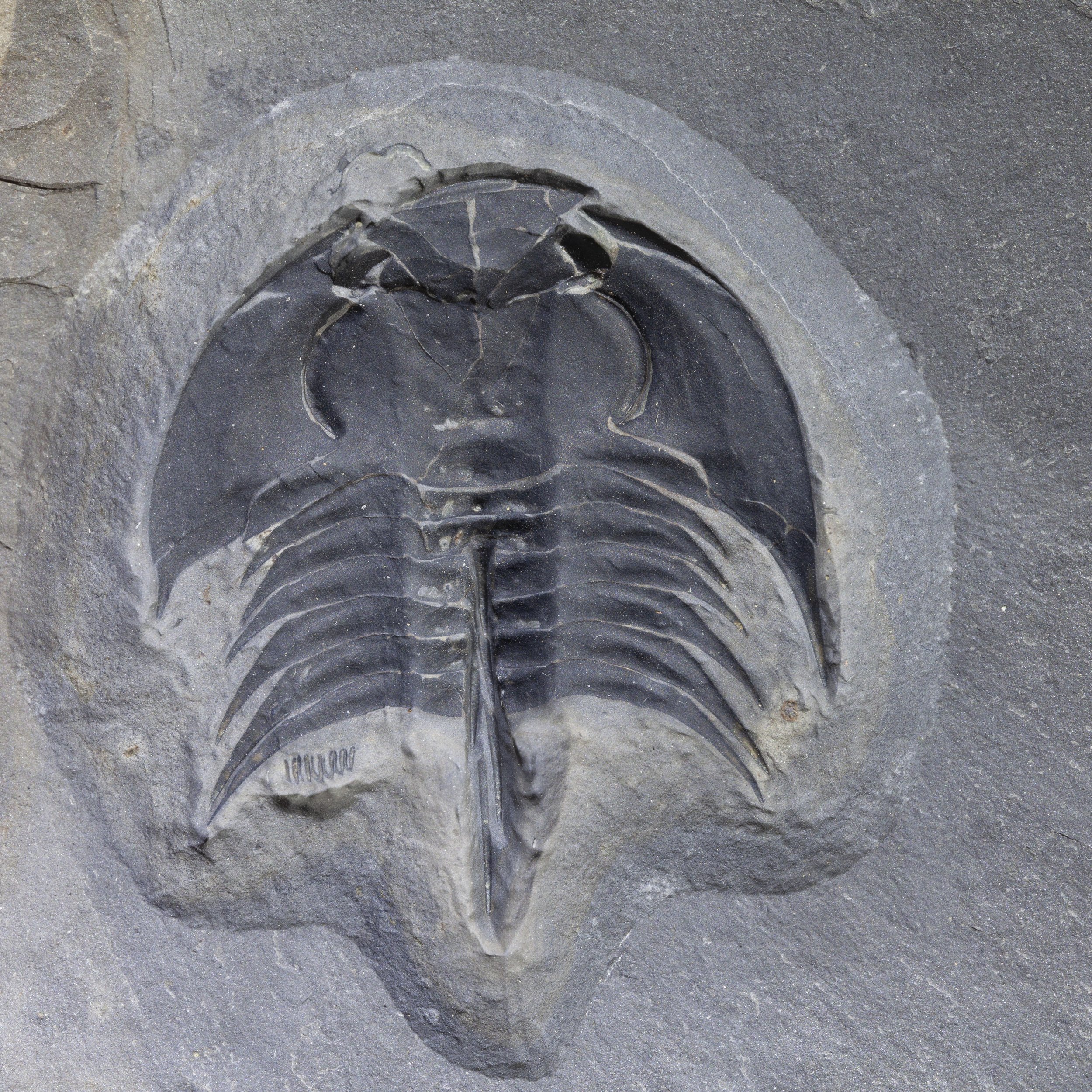
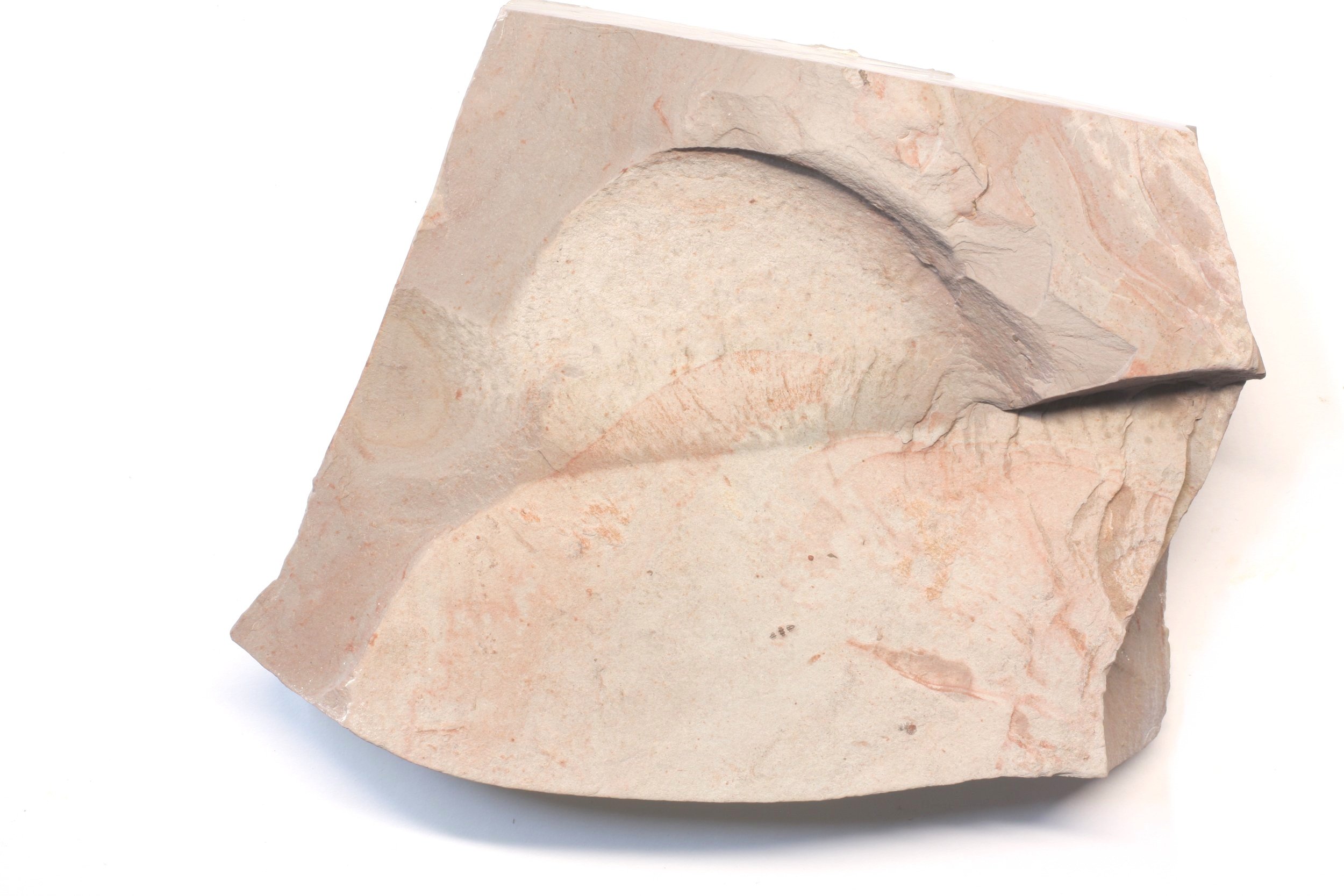
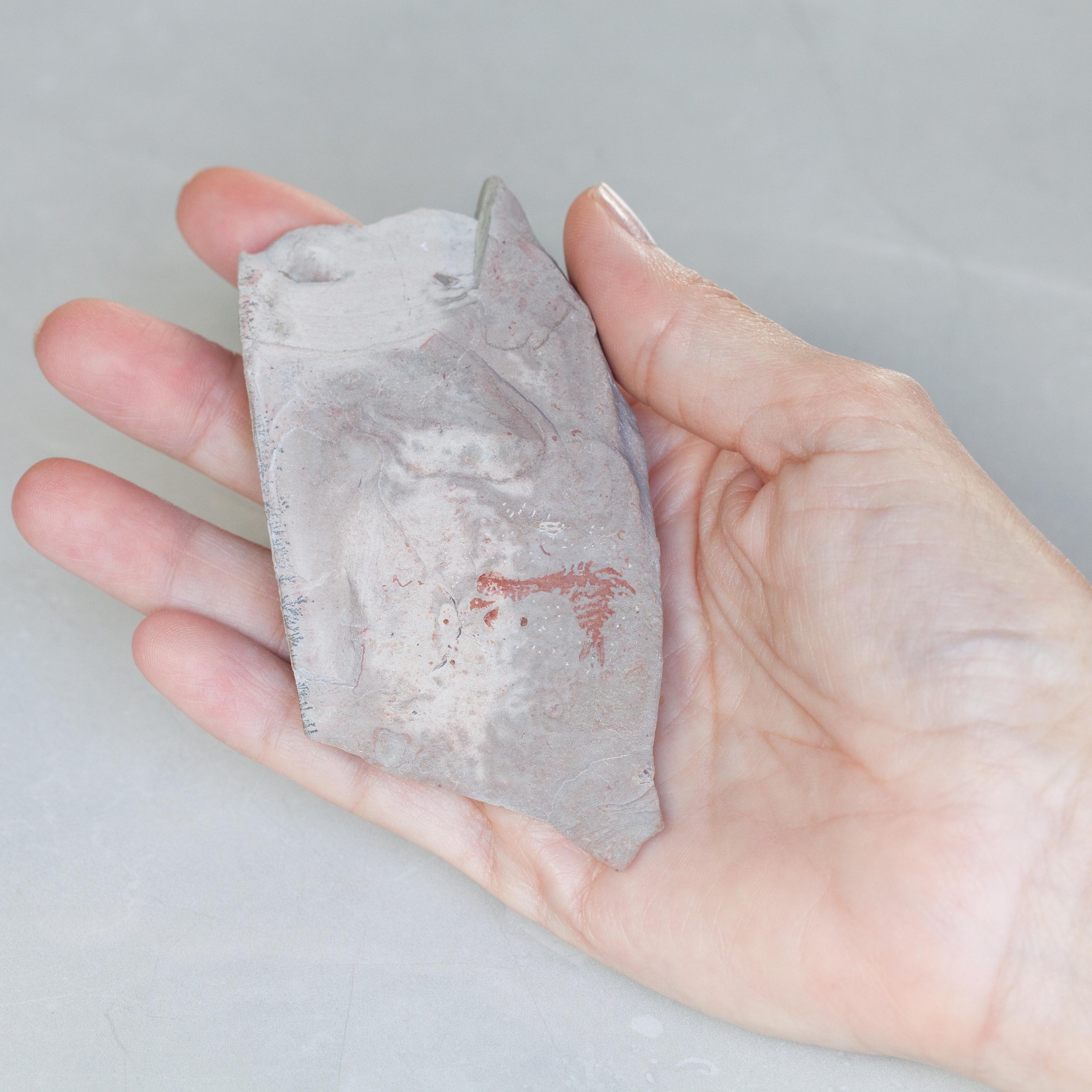
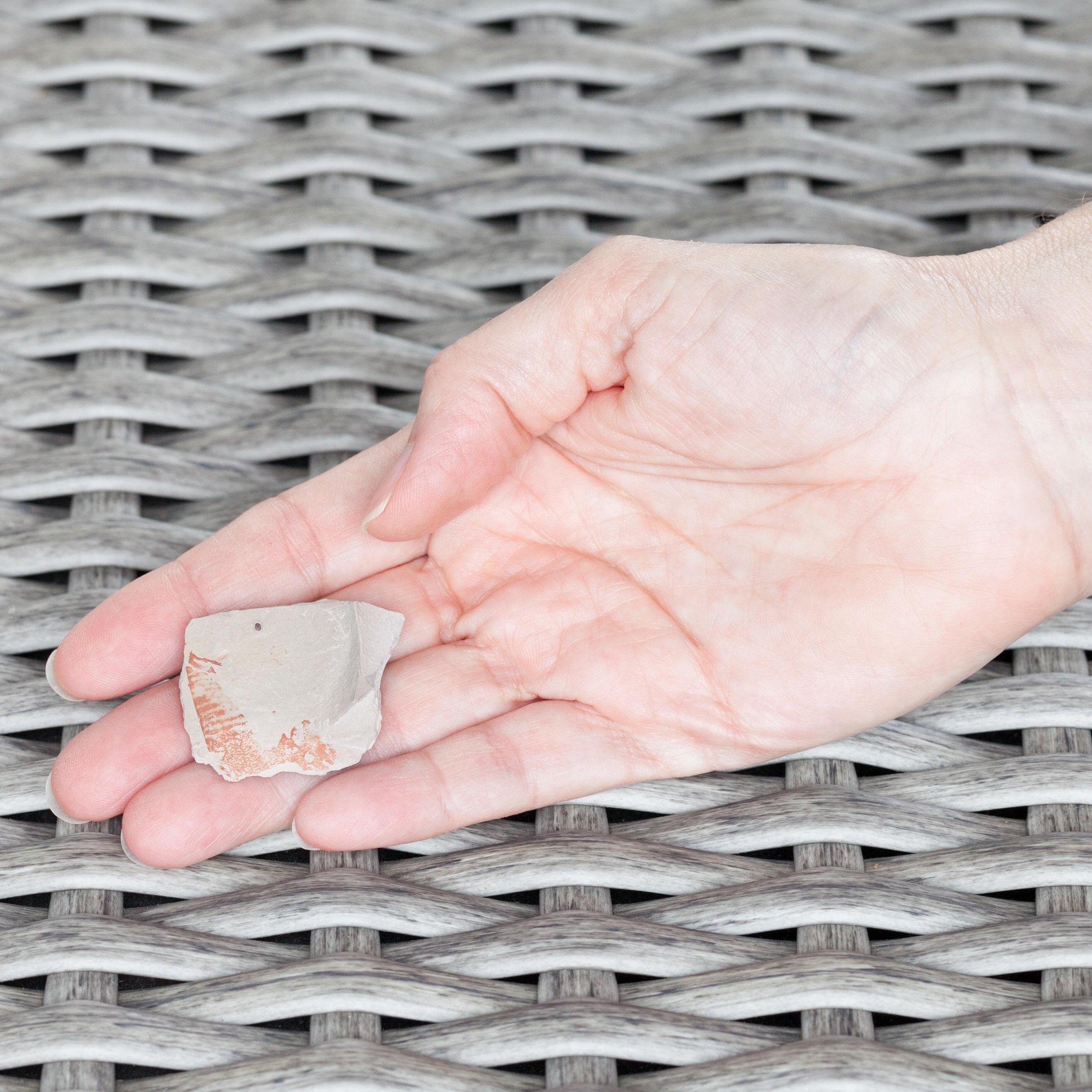
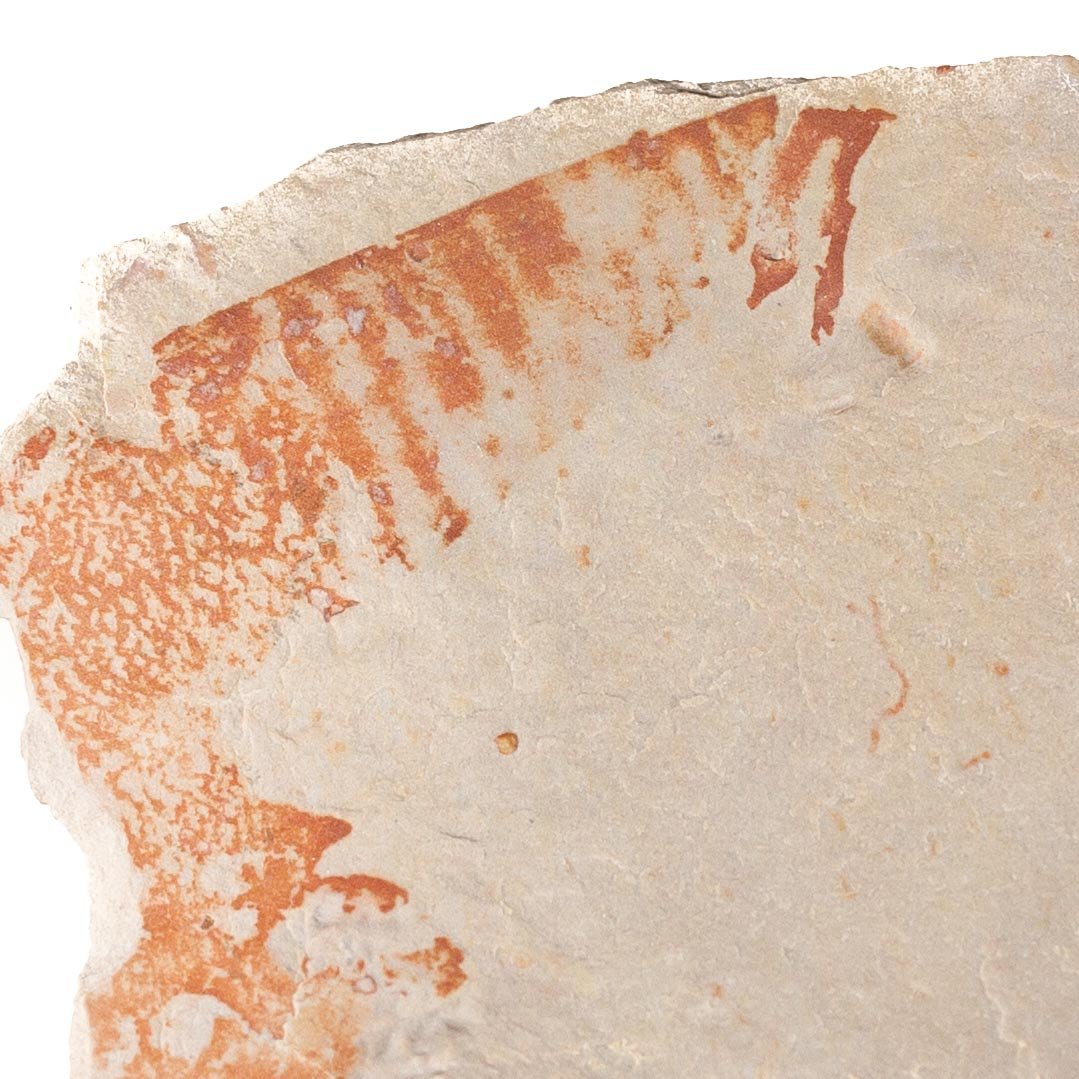
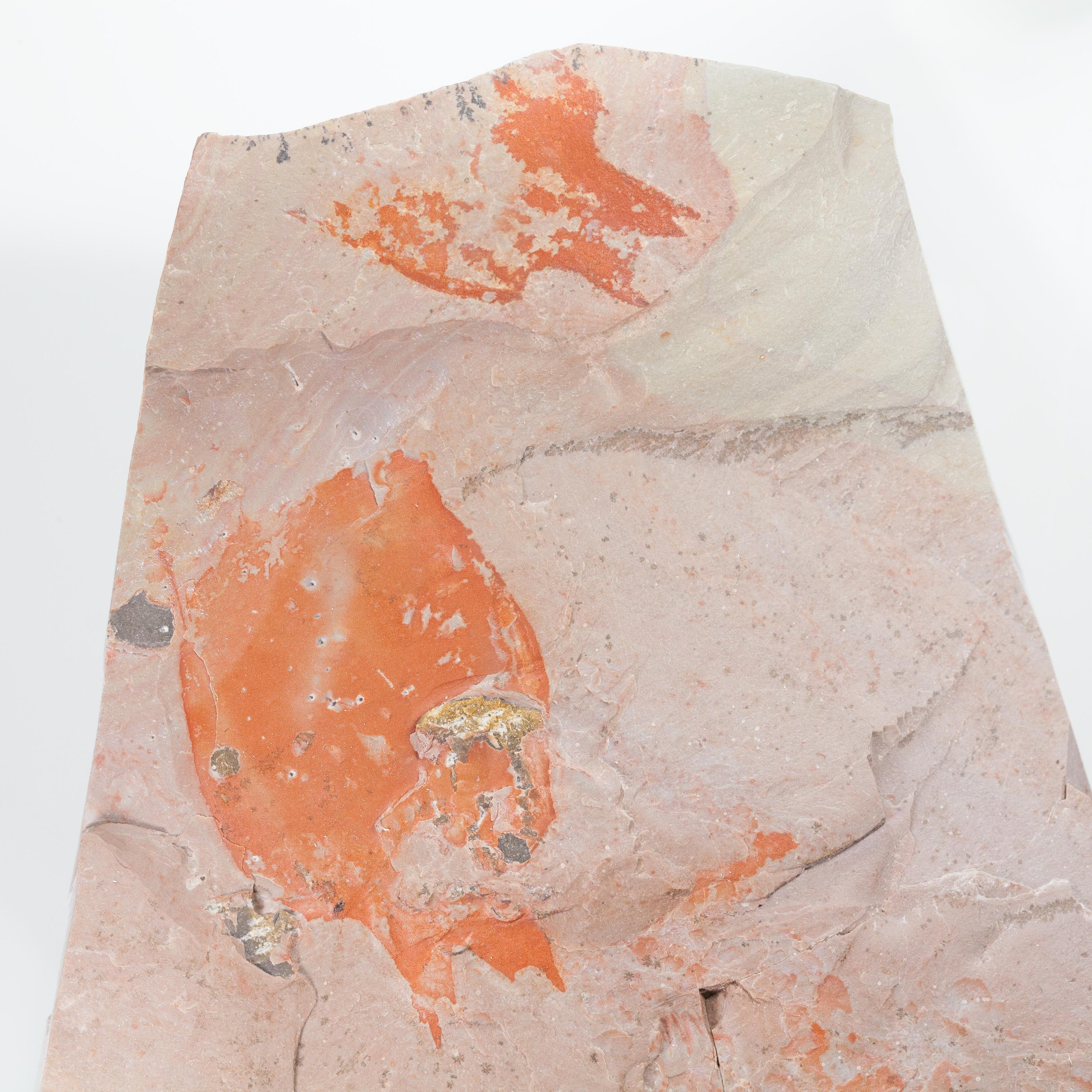
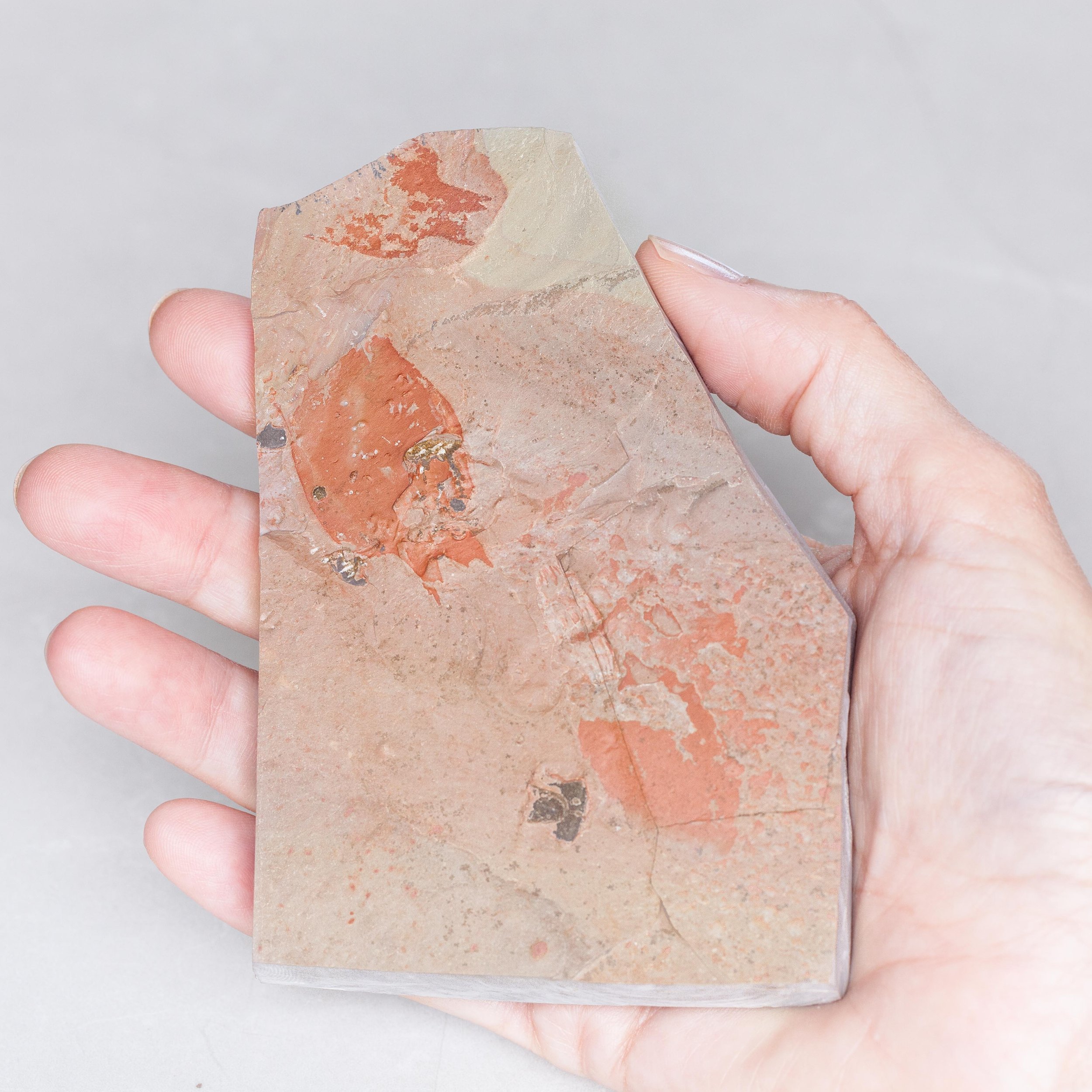
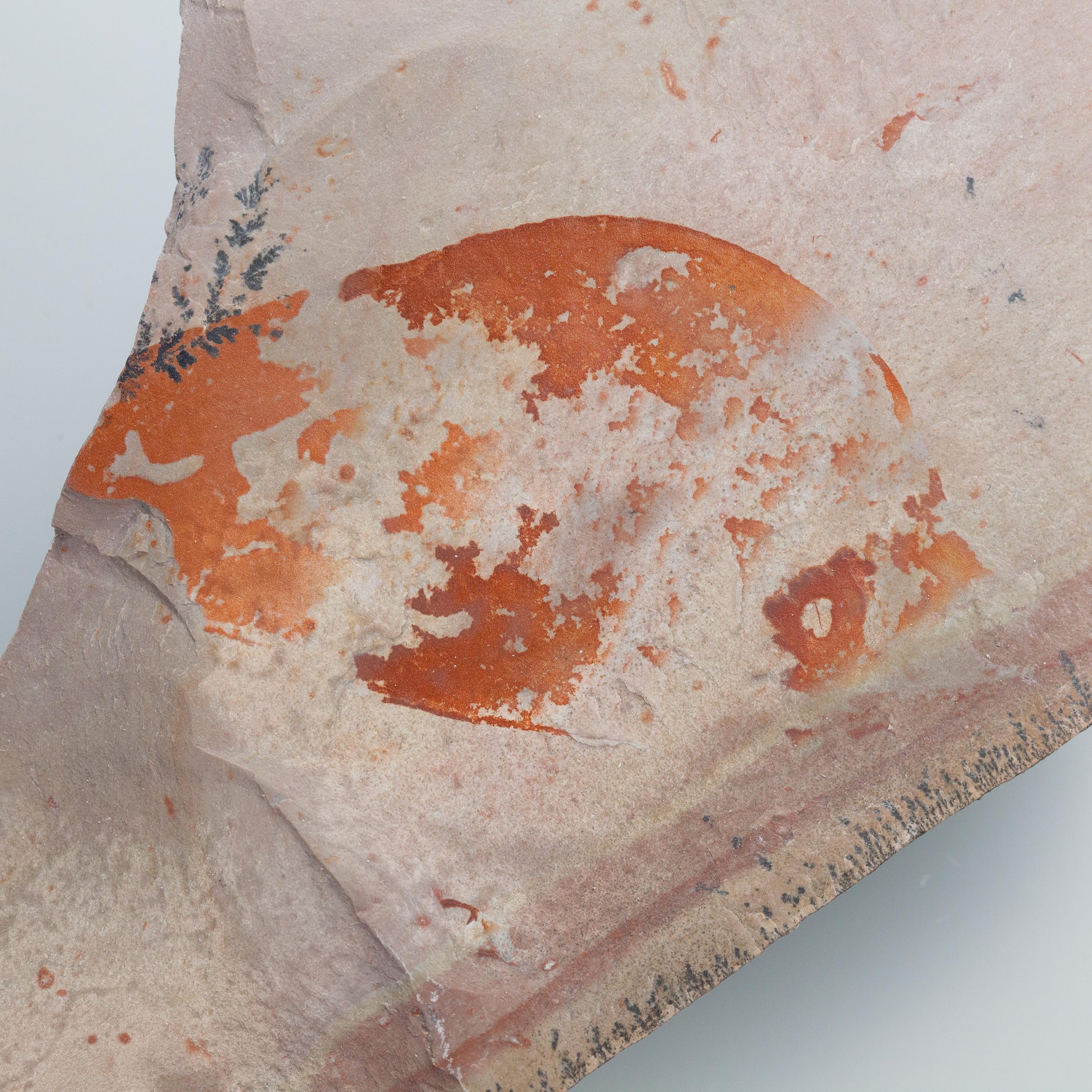
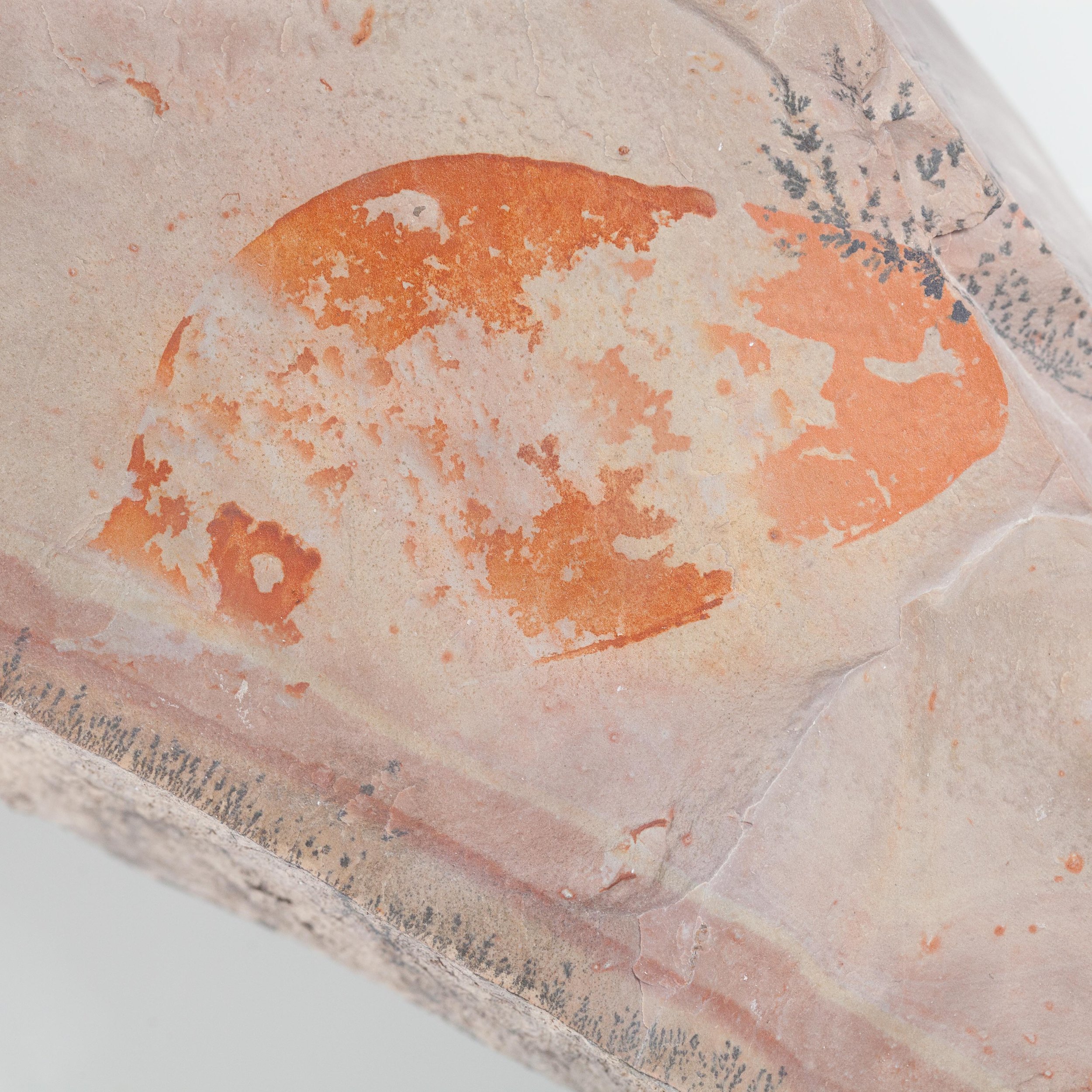
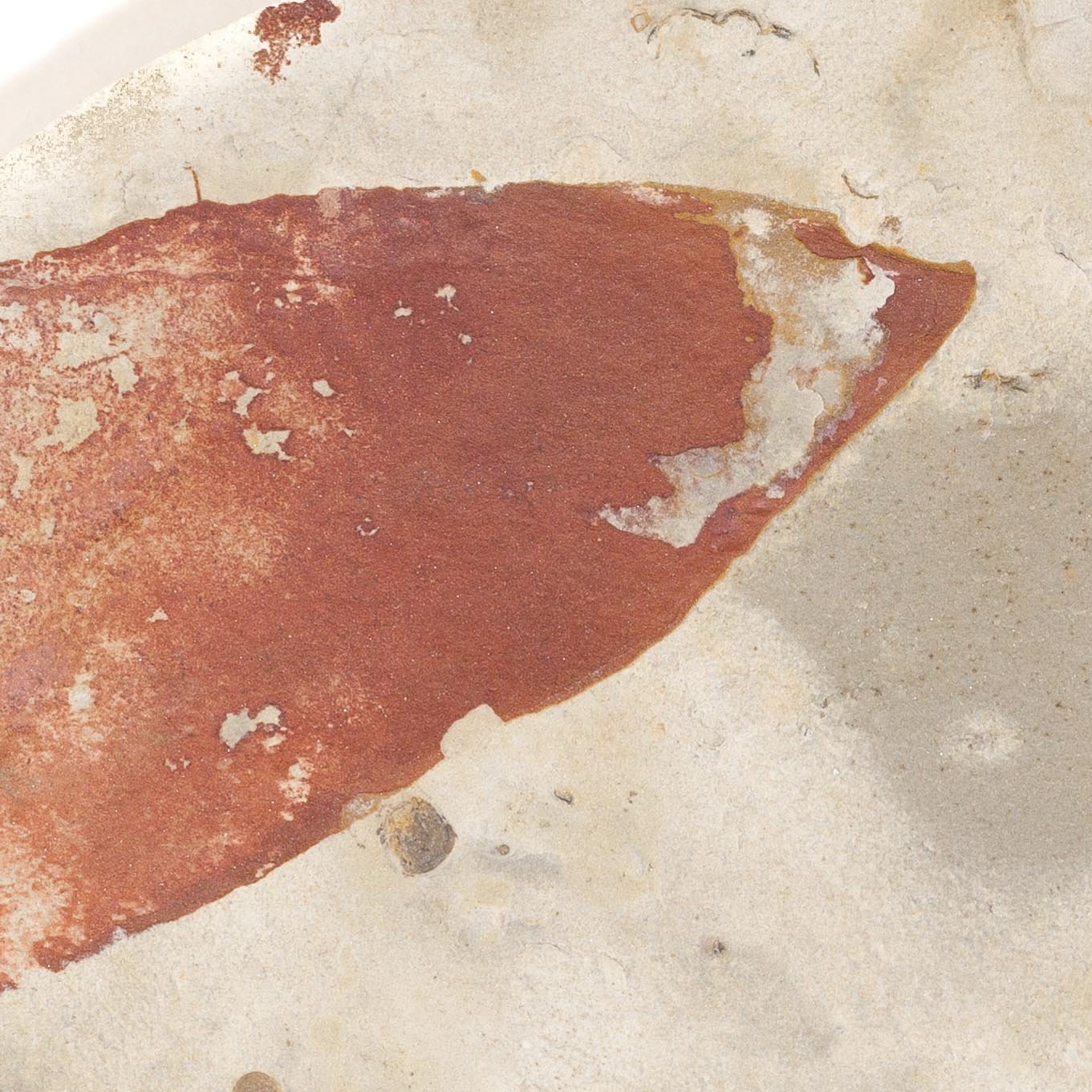
A head shield of a rare Anomalocaris cousin, Pahvantia hastata. This smaller Radiodont looked very similar to it’s more famous cousin, Anomalocaris, but sported a large cone-shaped head shield. These head shields are lost during molts. Pahvantia is thought to be a filter feeder, combing tiny organisms and detritus from the water column rather than being an active predator.
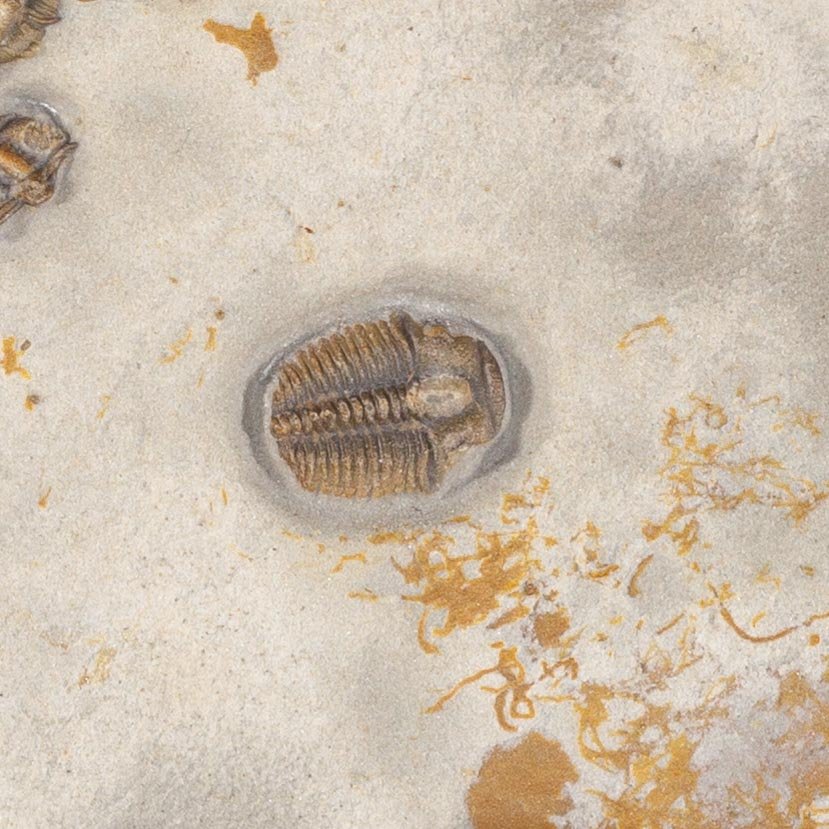
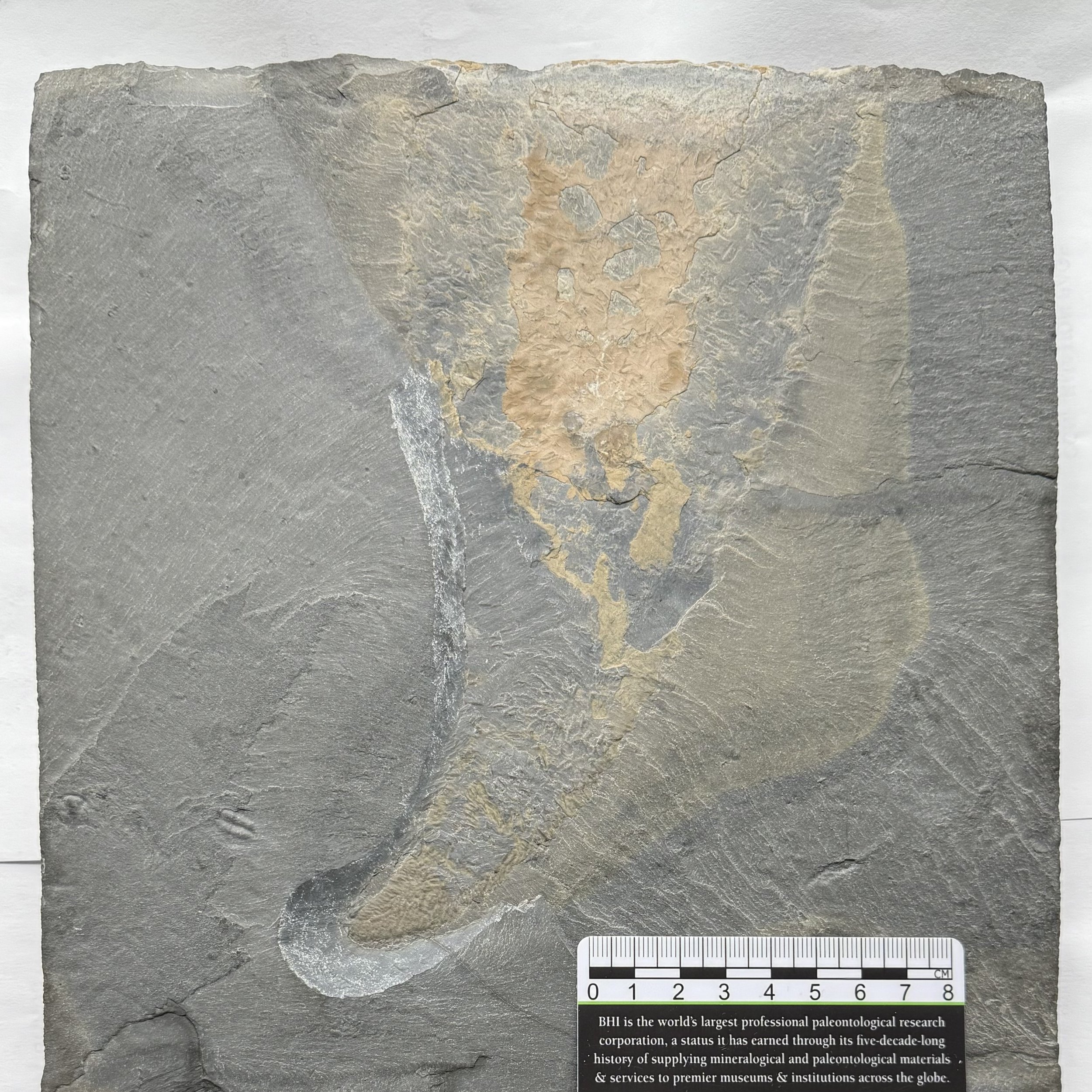
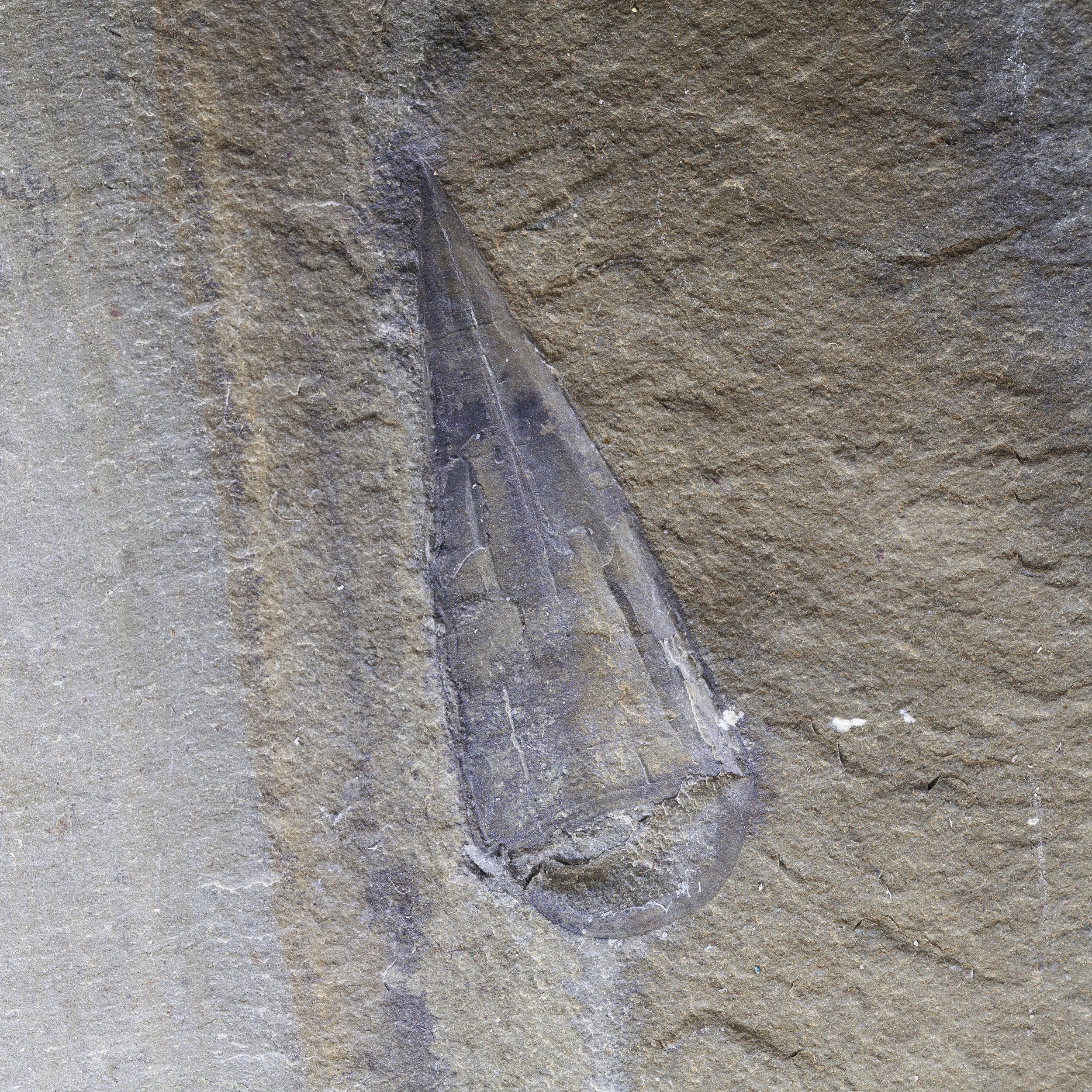
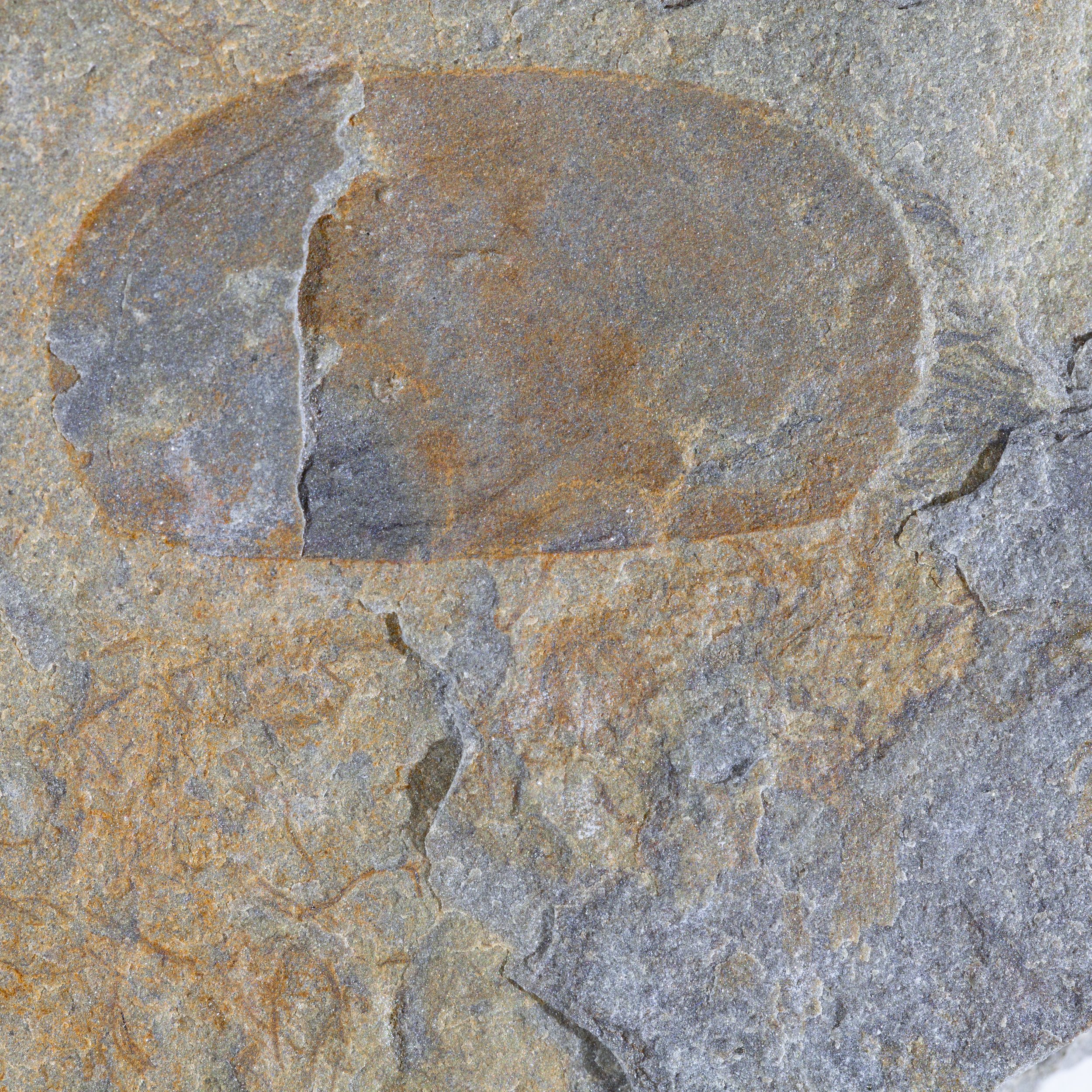
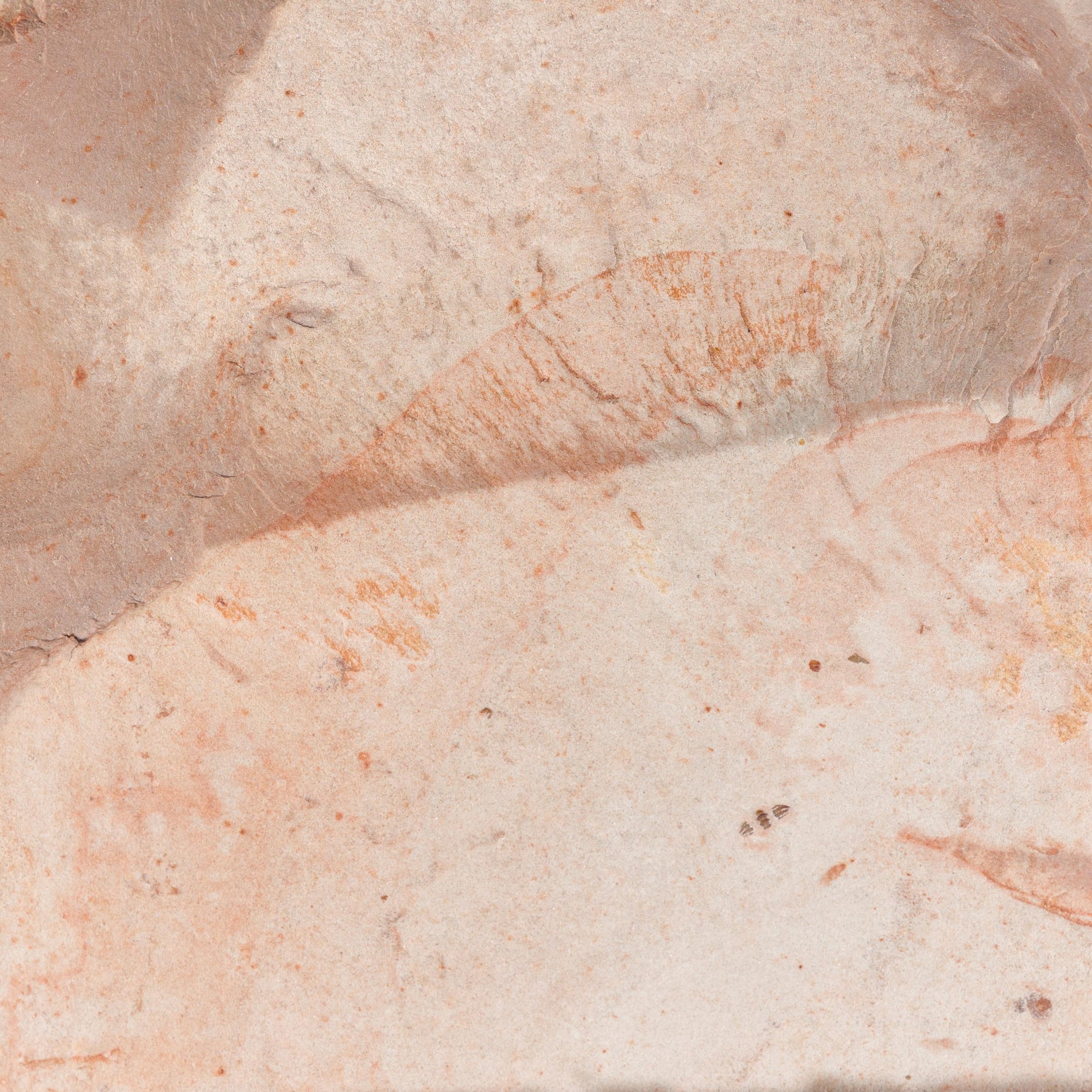
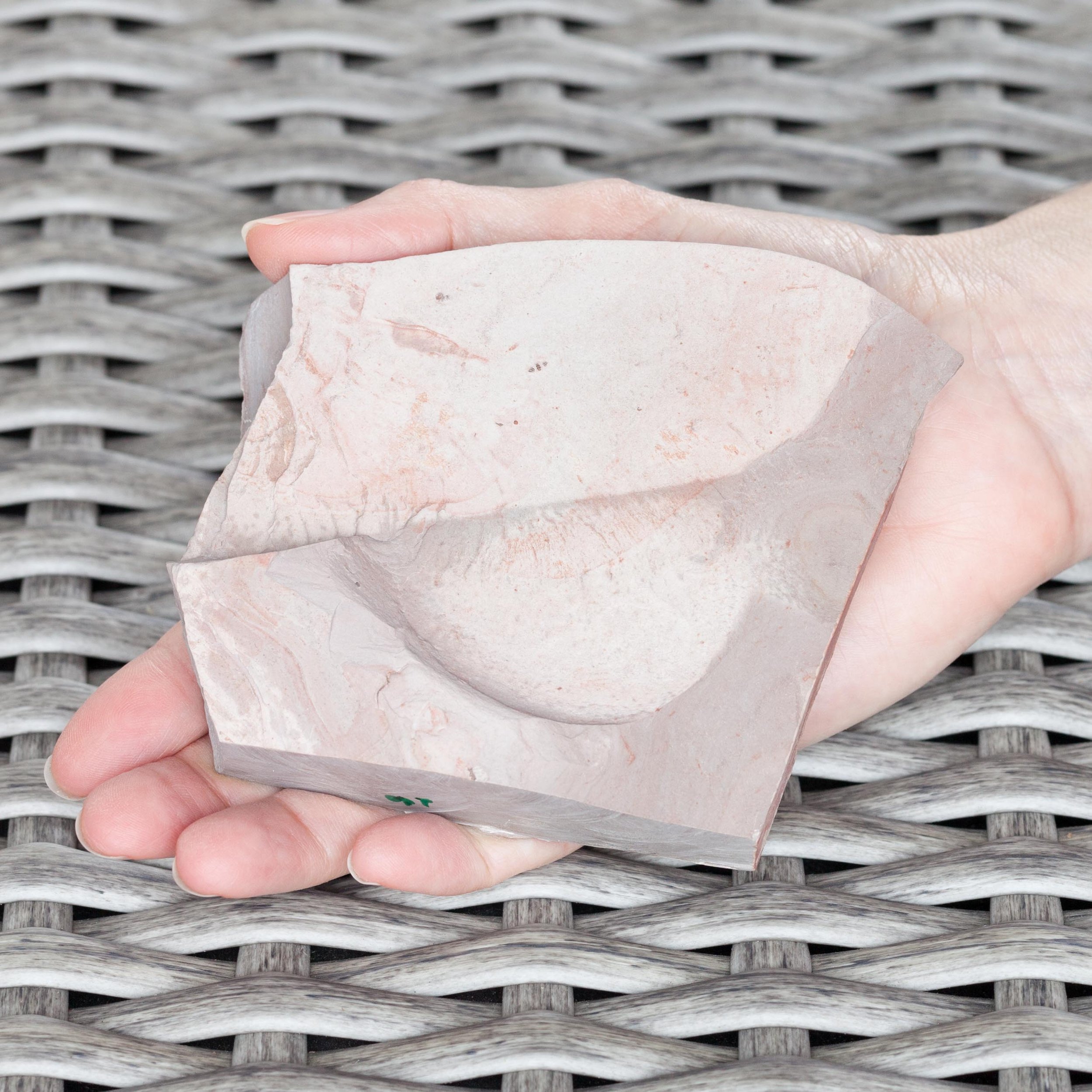
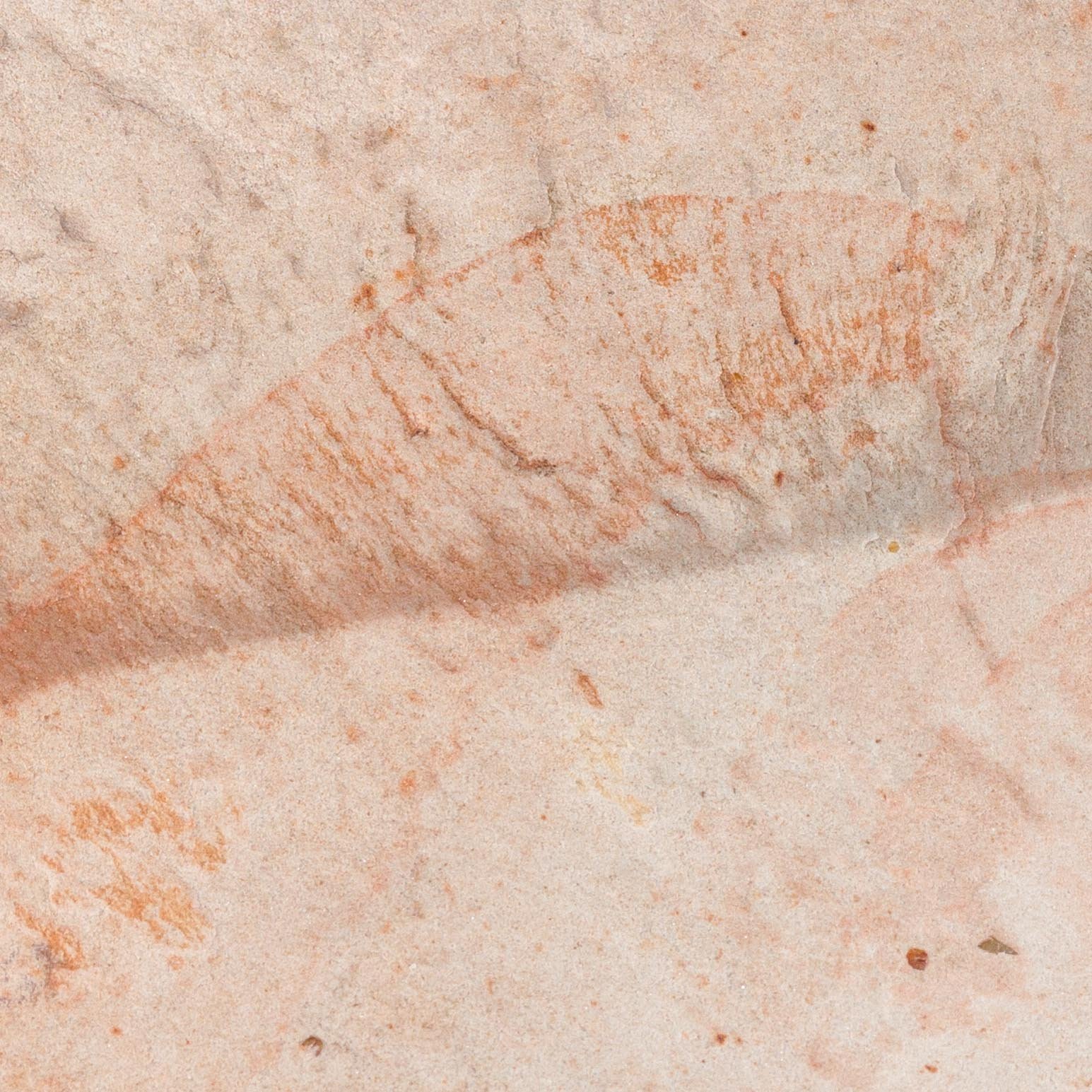
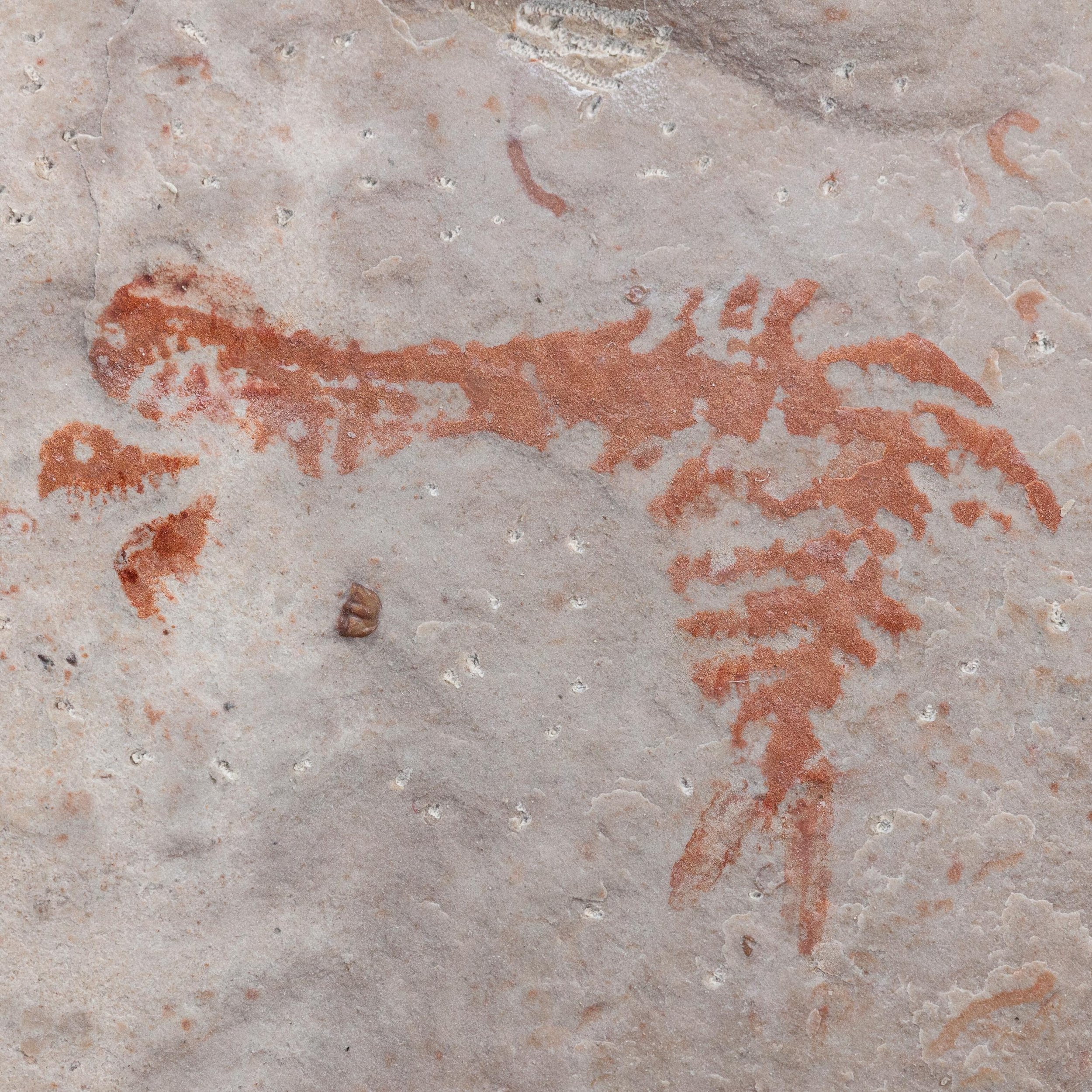
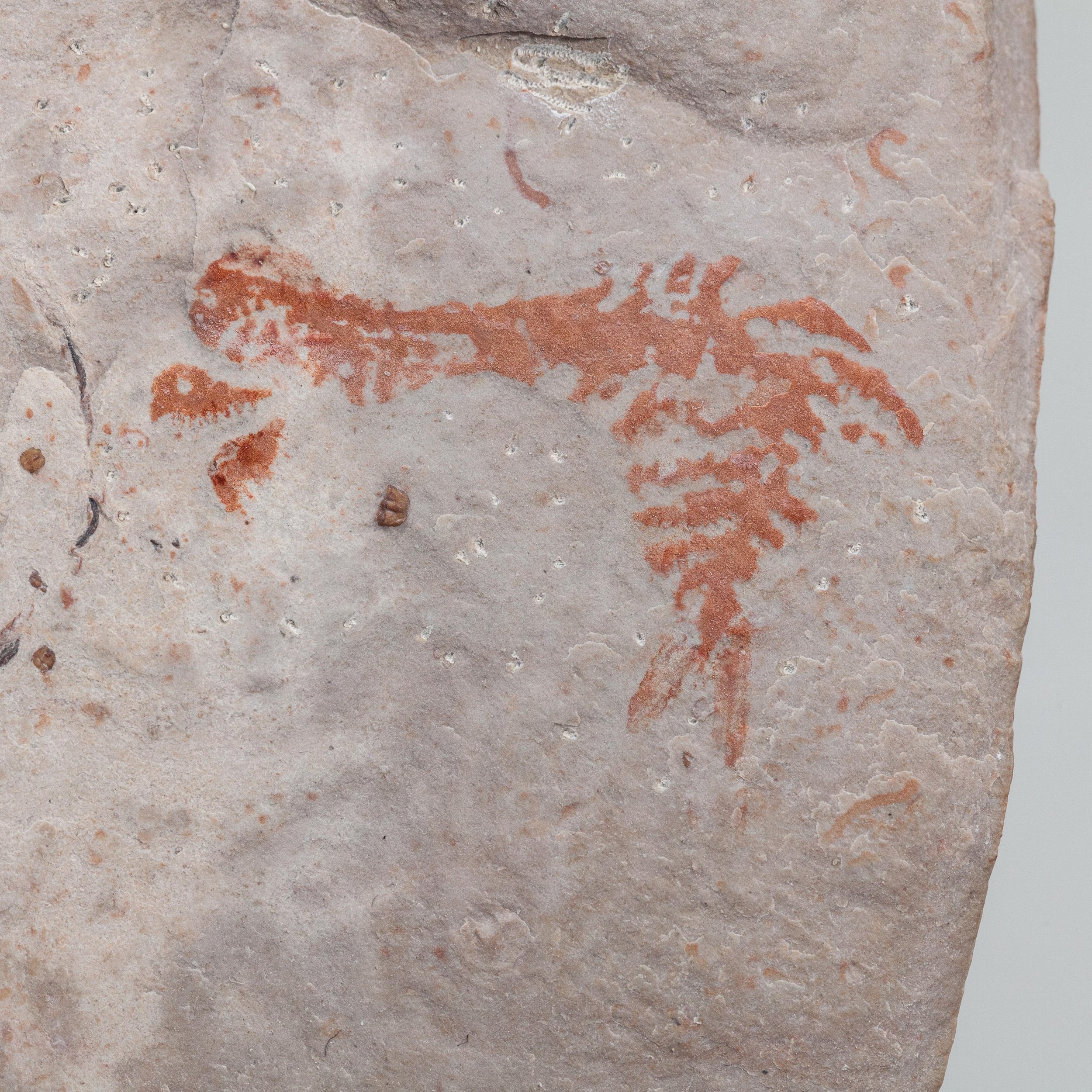
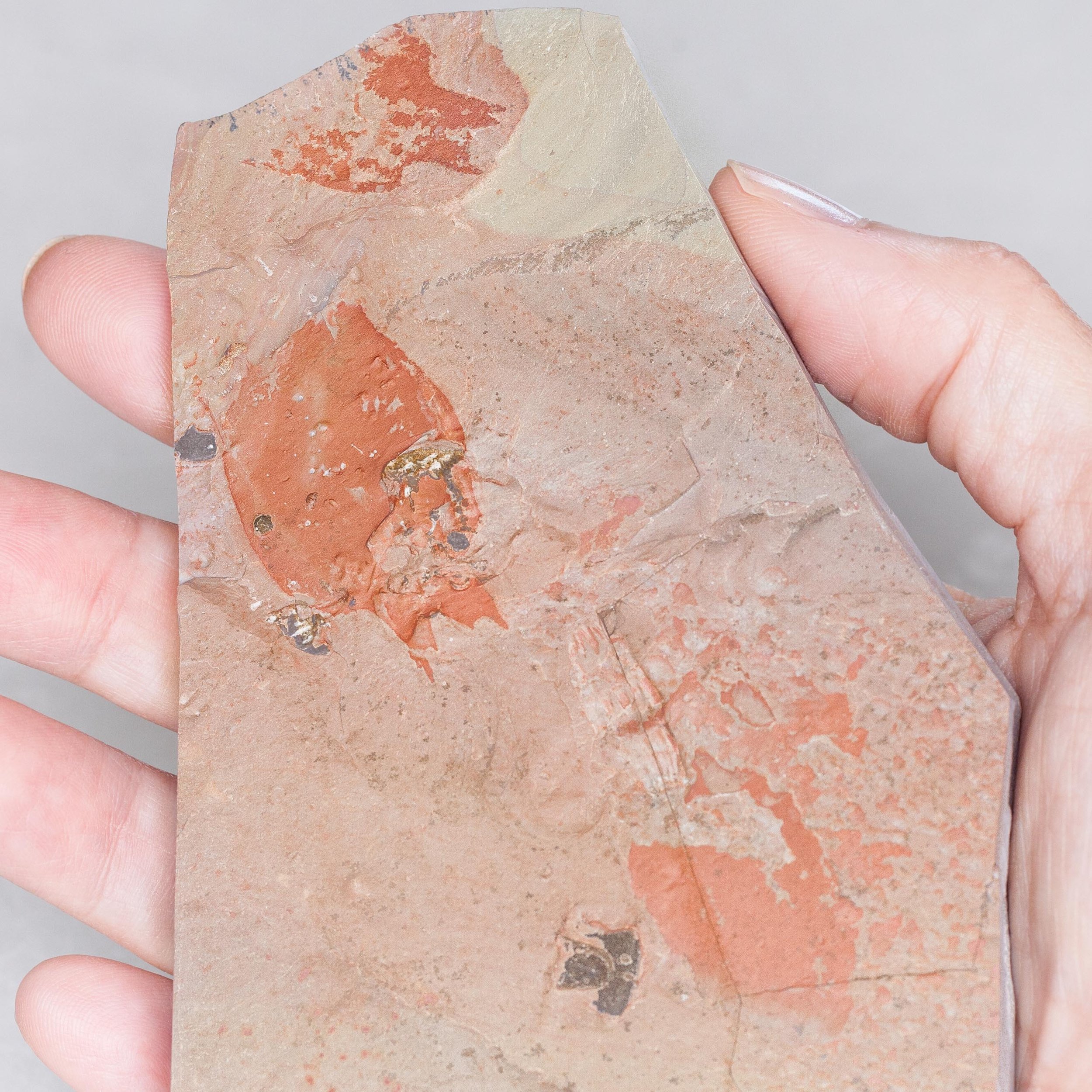
The head shield is preserved in vivid red and is accompanied by another rare Burgess Shale-type fossil, Dalyia racemata, which are the groups of branching algae to the upper right and right of the Pahvantia. Also on the plate are examples of the trilobite Bolaspidella housensis. So many great fossils in one piece!
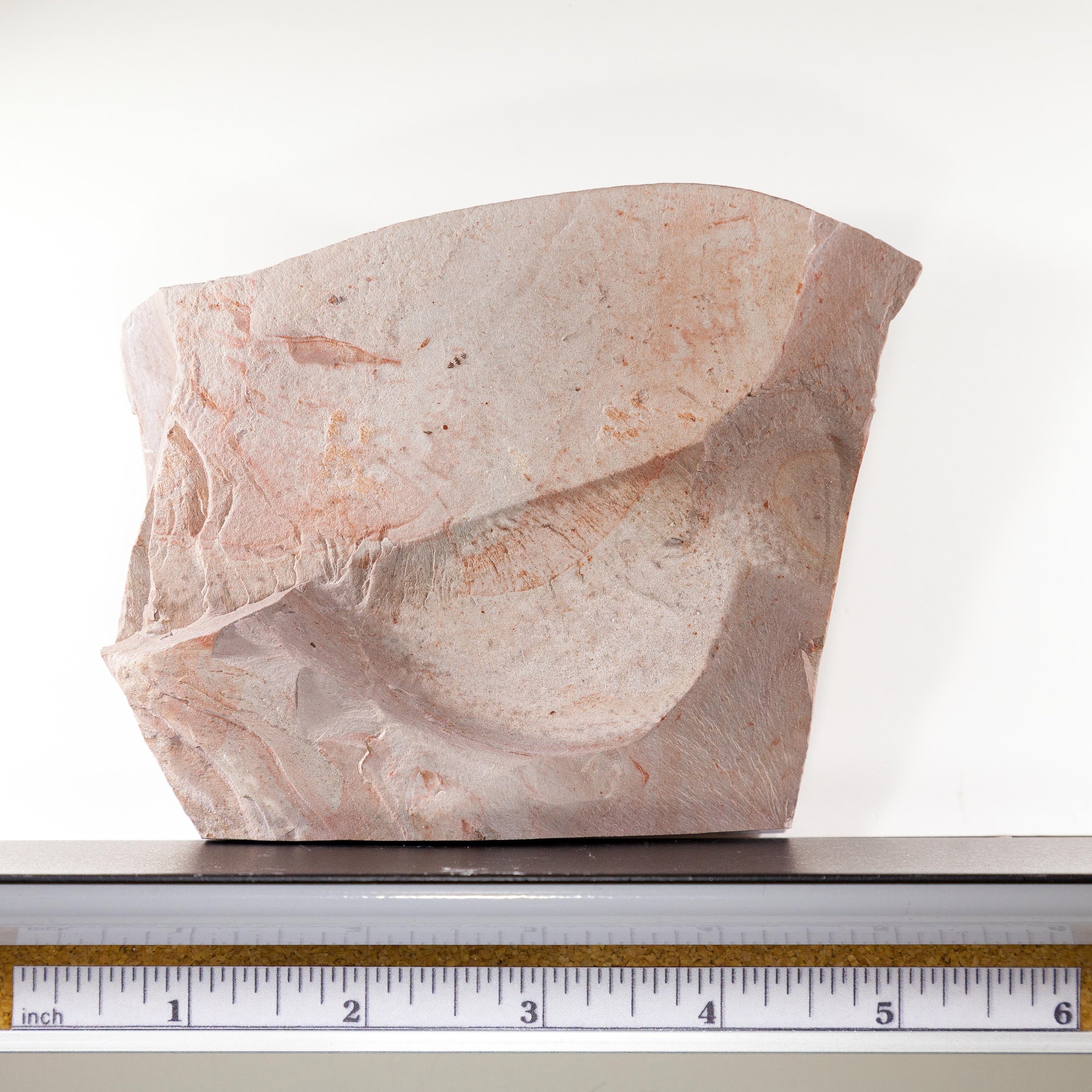
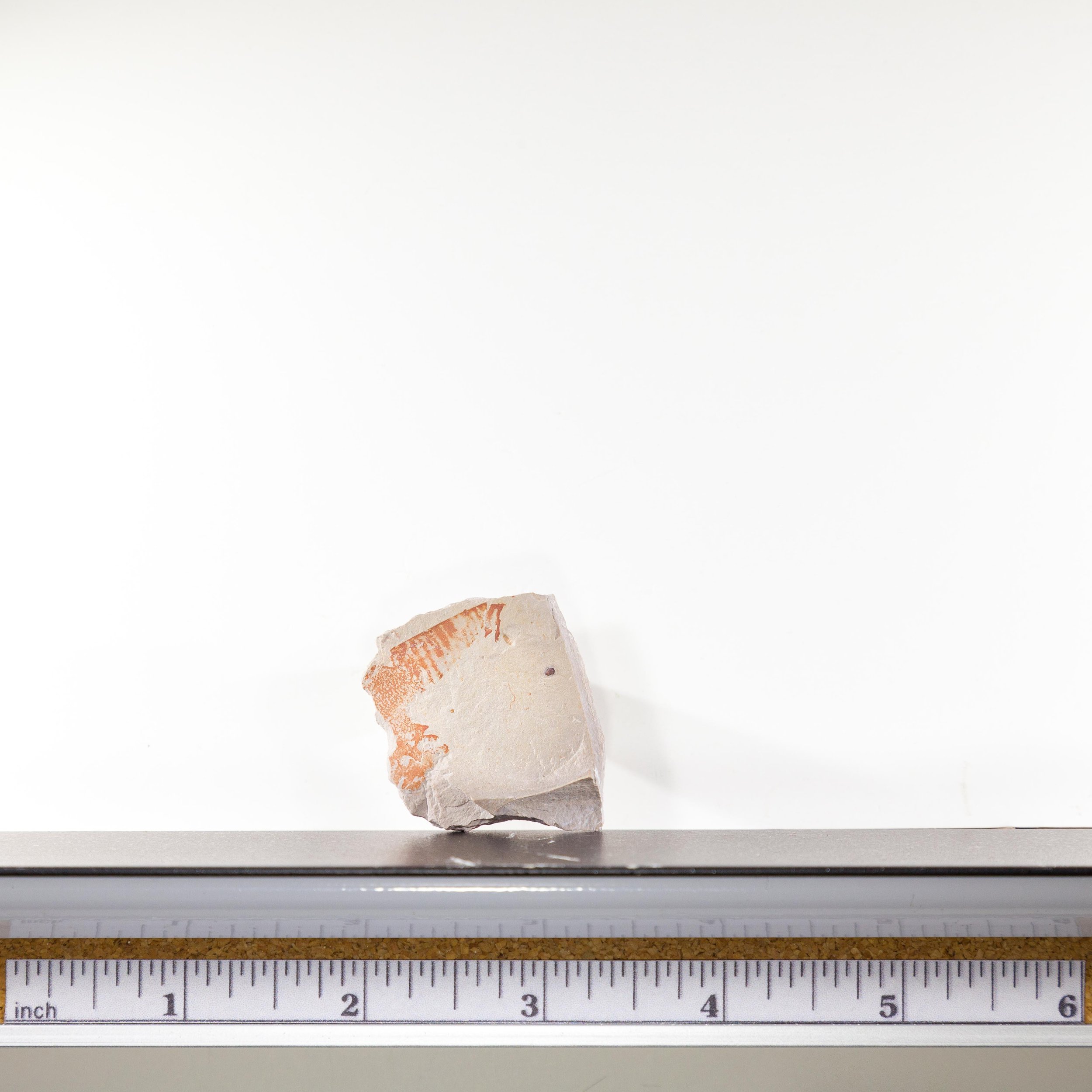
Full dimensions are listed below.
Vendor: Gold Bugs
SKU Number: SQ2630746
A head shield of a rare Anomalocaris cousin, Pahvantia hastata. This smaller Radiodont looked very similar to it’s more famous cousin, Anomalocaris, but sported a large cone-shaped head shield. These head shields are lost during molts. Pahvantia is thought to be a filter feeder, combing tiny organisms and detritus from the water column rather than being an active predator.
The head shield is preserved in vivid red and is accompanied by another rare Burgess Shale-type fossil, Dalyia racemata, which are the groups of branching algae to the upper right and right of the Pahvantia. Also on the plate are examples of the trilobite Bolaspidella housensis. So many great fossils in one piece!
Full dimensions are listed below.
Vendor: Gold Bugs
SKU Number: SQ2630746
A head shield of a rare Anomalocaris cousin, Pahvantia hastata. This smaller Radiodont looked very similar to it’s more famous cousin, Anomalocaris, but sported a large cone-shaped head shield. These head shields are lost during molts. Pahvantia is thought to be a filter feeder, combing tiny organisms and detritus from the water column rather than being an active predator.
The head shield is preserved in vivid red and is accompanied by another rare Burgess Shale-type fossil, Dalyia racemata, which are the groups of branching algae to the upper right and right of the Pahvantia. Also on the plate are examples of the trilobite Bolaspidella housensis. So many great fossils in one piece!
Full dimensions are listed below.
Additional Information
Pahvantia hastata was a Radiodont with raptorial fore-limbs used for filter feeding on microscopic organisms floating near the ocean surface. It has been suggested that the first planktonic animals in the Cambrian initiated the biological pump, which, in turn, fueled the diversification of complex animal communities on the seafloor.
The Radiodonts were a group of Arthropods that appeared early in the Cambrian and appear to have been the first free-swimming raptorial predators, a role subsequently taken on by animals such as Sharks, Fish, Squid, and marine Tetrapods, which appeared to place them firmly at the top of the Cambrian food-chain. These Radiodonts had rather complex exoskeletons, which tended to become disarticulated before being preserved.
Recently, large Radiodonts from the early Cambrian have been discovered that have feeding organs adapted not for raptorial predation but for filter feeding. Filter feeding has repeatedly appeared in the largest members of other groups of raptorial marine predators, including Sharks, Whales and several types of Fish, making this a predictable occurrence in large raptorial Radiodonts, a view that was supported by the discovery of a second such species, the two meter long Aegirocassis from the Early Ordovician.
References:
Pahvantia hastata - Sciency Thoughts
Pahvantia hastata - University of New England